|
自最近几十年来,心脏病已成为一个大问题,许多人由于某些健康问题而死亡。因此,心脏病不能掉以轻心。通过在初始阶段分析或监测ECG信号,可以预防这种疾病。因此,我们制作了这个小项目,即使用ECG传感器AD8232和Arduino进行图形监控。
AD8232是一款精巧的小芯片,用于测量心脏的电活动。这种电活动可以绘制为ECG或心电图。心电图检查有助于诊断各种心脏状况。
因此,在本篇文章中,我们将AD8232 ECG传感器与Arduino进行连接,并在串口绘图仪或Processing IDE上观察ECG信号。
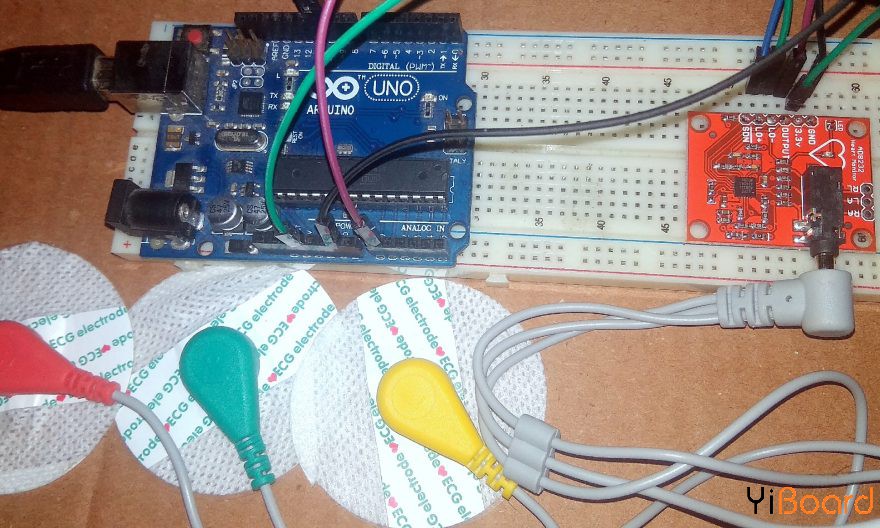
所需的组件 ● Arduino Uno开发板 ● ECG模块AD8232 ● 心电电极 ● ECG电极连接器-3.5毫米 ● 电源 ● 连接线
什么是心电图?
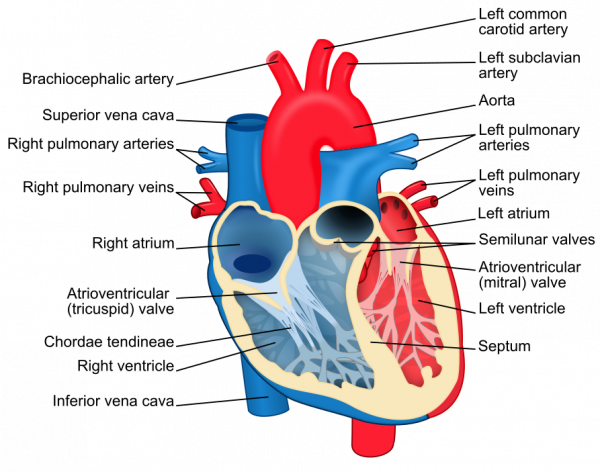
ECG是心脏电信号的纸质或数字记录,也称为心电图或EKG。 ECG用于确定心率、心律以及有关心脏状况的其他信息。 ECG用于帮助诊断心律不齐、心脏病发作、起搏器功能和心力衰竭。
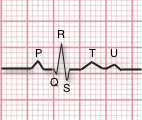
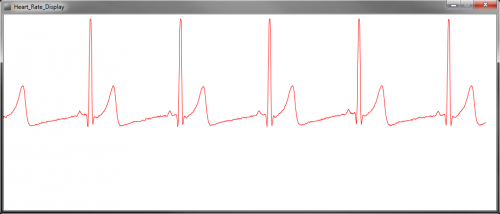
可以通过研究波形的成分来分析ECG。这些波形分量指示心脏电活动。 ECG追踪的第一个向上是P波。它表示心房收缩。QRS复数以Q(向下的小偏转)开始,然后是较大的向上的偏转(峰值(R)),然后是向下的S波。 QRS波群表明心室去极化和收缩。最后,T波通常是较小的向上波形,代表心室重新极化。
心电图的医疗用途 心电图检查可能是找出高血压是否对心脏或血管造成任何损害的有用方法。因此,初次诊断为高血压时,可能会要求您进行ECG检查。
心电图读数可以检测到的一些东西是: ● 胆固醇阻塞心脏的血液供应 ● 过去的心脏病 ● 心脏一侧扩大 ● 心律异常
AD8232心电图传感器 该传感器是一种经济高效的模块,用于测量心脏的电活动。可以将这种电活动绘制为ECG或心电图,并以模拟读数形式输出。 ECG可能非常嘈杂,单通道心率监测器AD8232用作运算放大器,可帮助轻松地从PR和QT间隔获得清晰的信号。
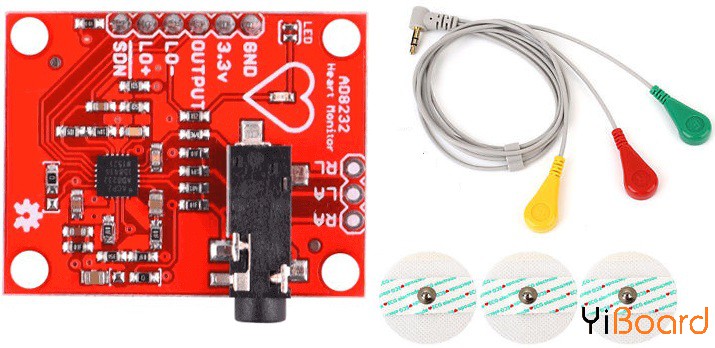
AD8232是一款集成的信号调理模块,用于ECG和其他生物电势测量应用。它设计用于在存在噪声的情况下(例如由运动或远程电极放置产生的情况)提取、放大和过滤小的生物电势信号。
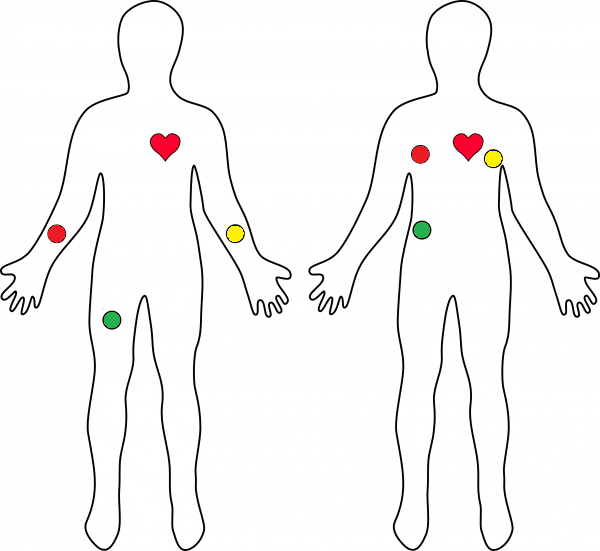
AD8232模块引出九个连接线,您可以将其焊接到引脚、电线或其他连接器上。 SDN、LO +、LO-、OUTPUT、3.3V、GND提供了必要的引脚,用于通过Arduino或其他开发板操作此显示器。该板上还提供了RA(右臂)、LA(左臂)和RL(右腿)引脚,用于连接和使用您自己的自定义传感器。此外,还有一个LED指示灯会随着心跳的节奏而跳动。
Arduino与ECG传感器AD8232之间的连接电路图 AD8232心率监测器从IC引出九个连接线:
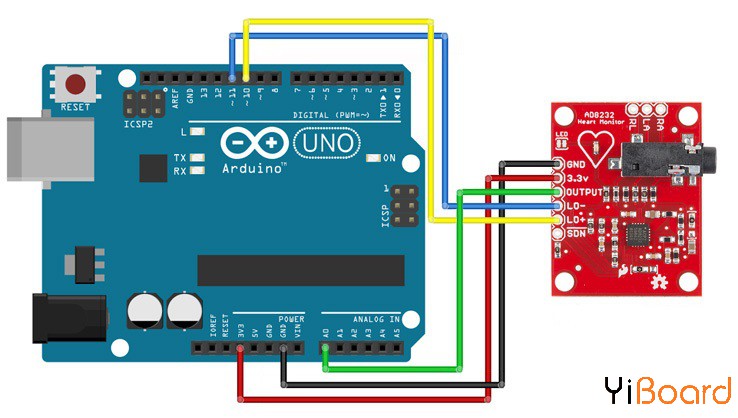
我们将板上的9个引脚中的5个连接到Arduino。您需要的五个引脚分别标记为GND、3.3v、OUTPUT、LO-和LO +。
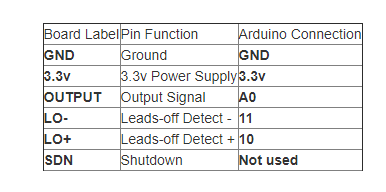
AD8232 ECG传感器在人体上的放置 建议在放到身体上之前,先将传感器垫卡在引线上。垫离心脏越近,测量越好。电缆采用颜色编码,以帮助识别正确的位置。 红色:RA(右臂) 黄色:LA(左臂) 绿色:RL(右腿)
Arduino源代码/程序 - void setup() {
- // initialize the serial communication:
- Serial.begin(9600);
- pinMode(10, INPUT); // Setup for leads off detection LO +
- pinMode(11, INPUT); // Setup for leads off detection LO -
- }
- void loop() {
- if((digitalRead(10) == 1)||(digitalRead(11) == 1)){
- Serial.println('!');
- }
- else{
- // send the value of analog input 0:
- Serial.println(analogRead(A0));
- }
- //Wait for a bit to keep serial data from saturating
- delay(1);
- }
Processing IDE源代码/程序 上传代码后,您可以在串口监视器和串口绘图仪上看到该值。
但是,如果您需要分离图形并想在Processing IDE上绘制它,则可以使用下面的代码。 - import processing.serial.*;
- Serial myPort; // The serial port
- int xPos = 1; // horizontal position of the graph
- float height_old = 0;
- float height_new = 0;
- float inByte = 0;
- int BPM = 0;
- int beat_old = 0;
- float[] beats = new float[500]; // Used to calculate average BPM
- int beatIndex;
- float threshold = 620.0; //Threshold at which BPM calculation occurs
- boolean belowThreshold = true;
- PFont font;
- void setup () {
- // set the window size:
- size(1000, 400);
- // List all the available serial ports
- println(Serial.list());
- // Open whatever port is the one you're using.
- myPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[2], 9600);
- // don't generate a serialEvent() unless you get a newline character:
- myPort.bufferUntil('\n');
- // set inital background:
- background(0xff);
- font = createFont("Ariel", 12, true);
- }
- void draw () {
- //Map and draw the line for new data point
- inByte = map(inByte, 0, 1023, 0, height);
- height_new = height - inByte;
- line(xPos - 1, height_old, xPos, height_new);
- height_old = height_new;
-
- // at the edge of the screen, go back to the beginning:
- if (xPos >= width) {
- xPos = 0;
- background(0xff);
- }
- else {
- // increment the horizontal position:
- xPos++;
- }
-
- // draw text for BPM periodically
- if (millis() % 128 == 0){
- fill(0xFF);
- rect(0, 0, 200, 20);
- fill(0x00);
- text("BPM: " + inByte, 15, 10);
- }
- }
- void serialEvent (Serial myPort)
- {
- // get the ASCII string:
- String inString = myPort.readStringUntil('\n');
- if (inString != null)
- {
- // trim off any whitespace:
- inString = trim(inString);
- // If leads off detection is true notify with blue line
- if (inString.equals("!"))
- {
- stroke(0, 0, 0xff); //Set stroke to blue ( R, G, B)
- inByte = 512; // middle of the ADC range (Flat Line)
- }
- // If the data is good let it through
- else
- {
- stroke(0xff, 0, 0); //Set stroke to red ( R, G, B)
- inByte = float(inString);
-
- // BPM calculation check
- if (inByte > threshold && belowThreshold == true)
- {
- calculateBPM();
- belowThreshold = false;
- }
- else if(inByte < threshold)
- {
- belowThreshold = true;
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- void calculateBPM ()
- {
- int beat_new = millis(); // get the current millisecond
- int diff = beat_new - beat_old; // find the time between the last two beats
- float currentBPM = 60000 / diff; // convert to beats per minute
- beats[beatIndex] = currentBPM; // store to array to convert the average
- float total = 0.0;
- for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++){
- total += beats[i];
- }
- BPM = int(total / 500);
- beat_old = beat_new;
- beatIndex = (beatIndex + 1) % 500; // cycle through the array instead of using FIFO queue
- }
|