|
按键状态变化检测(State Change Detection) 在使用按键的过程中,经常会遇到要根据按键按下的次数来做一些处理。要做到这一点,我们需要知道按键的状态何时从关断变成闭合,并且记录下这样的状态变化发生的次数。这就是所谓的状态变化检测或者是边沿检测。本示例展示了如何来检测状态变化,将相关信息发送到串行监视器( Serial Monitor),并且在四次状态变化时来点亮或熄灭LED指示灯。
所需硬件 - Arduino或者Genuino开发板 - 按钮开关
- 10k电阻
- 面包板 - 导线
电路连接方式
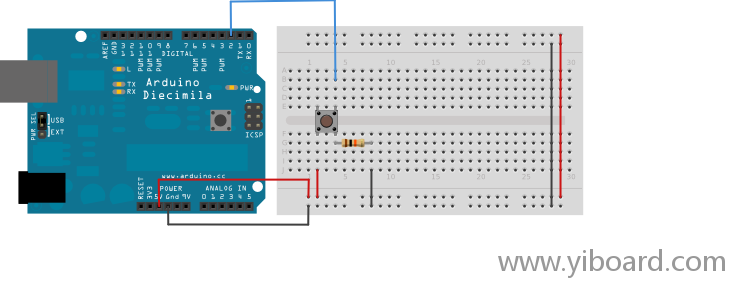
将三根导线连接到开发板。第一根导线将按键的一个引脚通过下拉电阻(用的是10k)连接到地。第二根导线将按键的另一个引脚连接到5V电源。第三根导线连接到数字IO引脚(2脚),通过该引脚来读取按键的状态。
当按钮处于开路状态(未按下)时,按键的两个引脚之间没有连接,所以该引脚连接到地(通过下拉电阻),并且读取时为低电平,或者0。当按键关闭(按下)时,两个引脚短接,使得该引脚连接到5V,因此读取时为高电平,或者1。
如果您断开数字I/O引脚的所有连接时,LED会无规律的闪烁。这是因为输入引脚处于悬浮状态,也就是说该引脚与电源或地之间没有固定的连接,并且会随机返回高电平或低电平。这就是为什么在电路中需要下拉电阻。
原理图
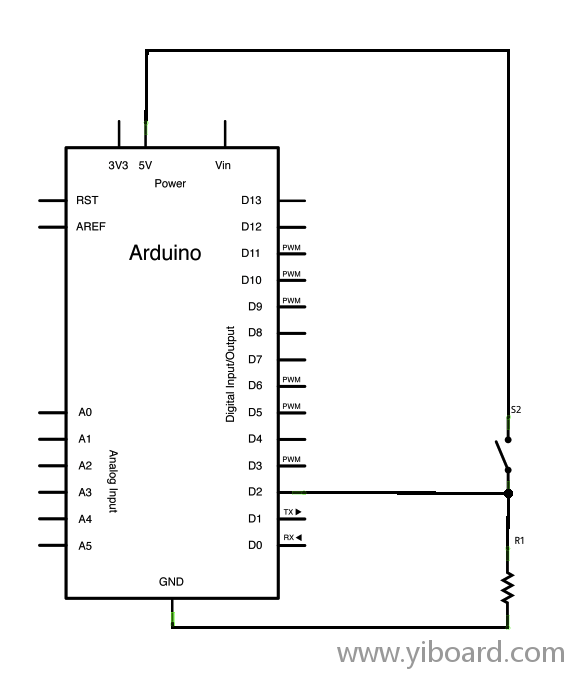
代码 下面的程序不断读取按键的状态。然后在主循环中与上次读取的按键状态进行对比。如果当前值与上次的按键状态不同,并且当前按键的状态为高电平,则表示按键从关断变成闭合。然后程序中增加一次按键按下的计数。
程序也检测按键按下的次数。如果该值是4的倍数,那么就会就将13脚的LED灯点亮。否则,LED熄灭。 - /*
- State change detection (edge detection)
- Often, you don't need to know the state of a digital input all the time,
- but you just need to know when the input changes from one state to another.
- For example, you want to know when a button goes from OFF to ON. This is called
- state change detection, or edge detection.
- This example shows how to detect when a button or button changes from off to on
- and on to off.
- The circuit:
- * pushbutton attached to pin 2 from +5V
- * 10K resistor attached to pin 2 from ground
- * LED attached from pin 13 to ground (or use the built-in LED on
- most Arduino boards)
- created 27 Sep 2005
- modified 30 Aug 2011
- by Tom Igoe
- This example code is in the public domain.
- http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/ButtonStateChange
- */
- // this constant won't change:
- const int buttonPin = 2; // the pin that the pushbutton is attached to
- const int ledPin = 13; // the pin that the LED is attached to
- // Variables will change:
- int buttonPushCounter = 0; // counter for the number of button presses
- int buttonState = 0; // current state of the button
- int lastButtonState = 0; // previous state of the button
- void setup() {
- // initialize the button pin as a input:
- pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
- // initialize the LED as an output:
- pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
- // initialize serial communication:
- Serial.begin(9600);
- }
- void loop() {
- // read the pushbutton input pin:
- buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
- // compare the buttonState to its previous state
- if (buttonState != lastButtonState) {
- // if the state has changed, increment the counter
- if (buttonState == HIGH) {
- // if the current state is HIGH then the button
- // wend from off to on:
- buttonPushCounter++;
- Serial.println("on");
- Serial.print("number of button pushes: ");
- Serial.println(buttonPushCounter);
- } else {
- // if the current state is LOW then the button
- // wend from on to off:
- Serial.println("off");
- }
- // Delay a little bit to avoid bouncing
- delay(50);
- }
- // save the current state as the last state,
- //for next time through the loop
- lastButtonState = buttonState;
- // turns on the LED every four button pushes by
- // checking the modulo of the button push counter.
- // the modulo function gives you the remainder of
- // the division of two numbers:
- if (buttonPushCounter % 4 == 0) {
- digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
- } else {
- digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
- }
- }
|  |手机版|YiBoard一板网
( 冀ICP备18020117号 )
|手机版|YiBoard一板网
( 冀ICP备18020117号 )